Monogenic Diseases Screening
Maternal/Paternal blood test for carrier screening
Why carrier screening is advisable?
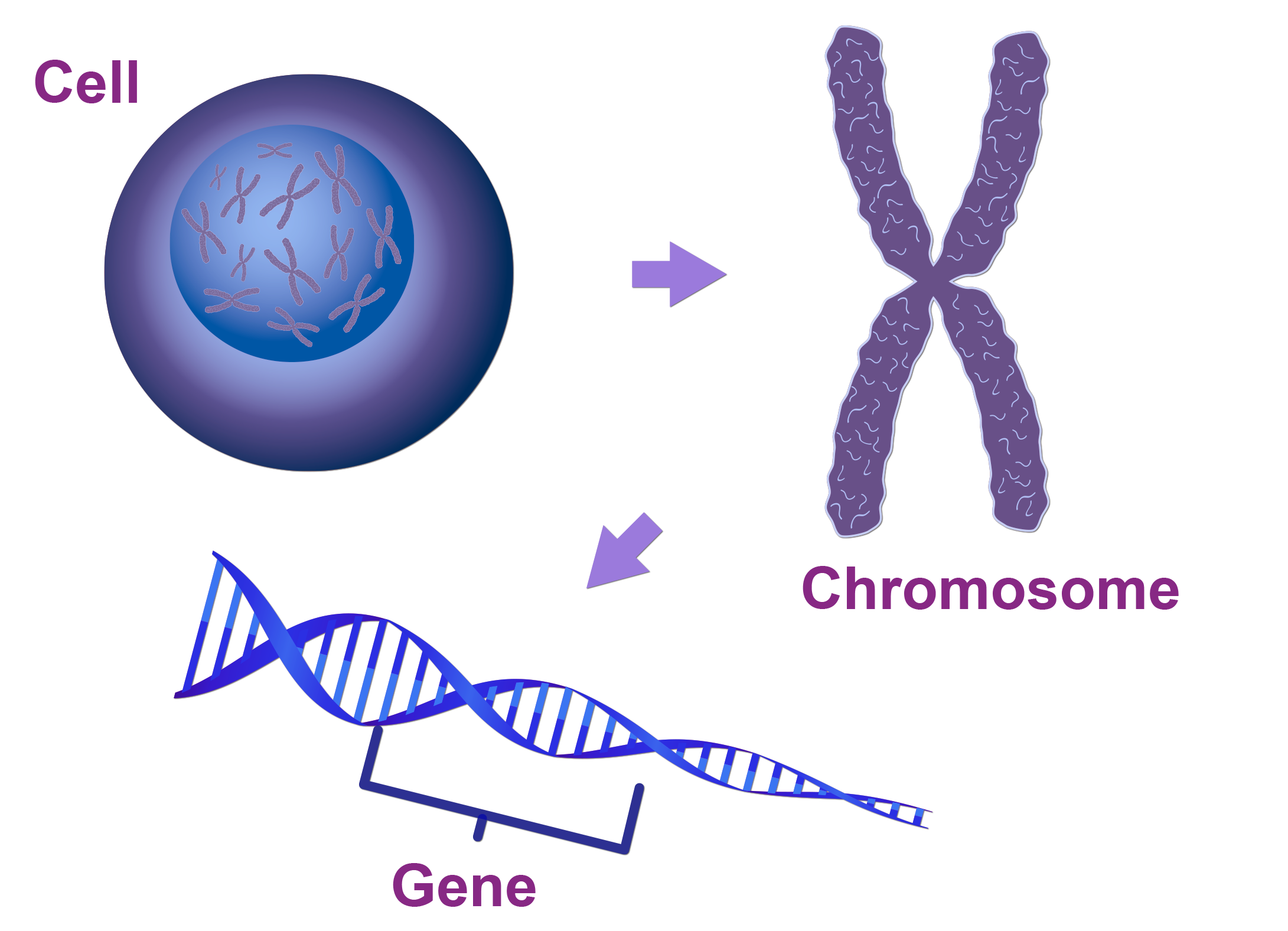
An individual inherits one copy of gene from the father and one copy from the mother. If the father or mother has a change (mutation) in one of the copies of a particular gene, he/she is known as a carrier of a disease.
Carriers are usually normal and have no family history of genetic diseases. It is usually when an abnormal child is born that the parents are aware they are carriers of a particular genetic disease.
If both parents are carriers of a particular genetic disease, there is a 25% chance of having abnormal child for that genetic disease for each pregnancy.
10 common genetic diseases detectable by carrier screening:
- α Thalassemia
- β Thalassemia
- Hereditary Hearing Loss and Deafness
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy
- Duchenne Muscular Atrophy
- Haemophilia A
- Haemophilia B
- Phenylketonuria
- Wilson Disease
- Glycogen Storage Disease
All women in preparation for pregnancy and all currently pregnant women should therefore have carrier screening test so as to avoid significant genetic disease passed to the child to be born.