Q&A
Q: How do I know whether I ovulate?
A:
If your menstrual cycle is between 28-35days, most often ovulation do occur.
You can have ovulation assessed in 3 ways
- Blood LH surge tests at around ovulation time
- Follicle tracking by ultrasound at around ovulation time
- Blood progesterone test 7 days after ovulation
Q: If I have regular menstrual cycles, will oral ovulation induction medicine improve
my pregnancy rate?
A:
Probably not. Regular monthly cycles indicate that you most probably ovulate regularly. Oral ovulation induction medicine like clomid may decrease the thickness of the inside lining of the uterus, making implantation of the embryo difficult.
Q: Is there medicine that can improve semen parameters?
A:
Poor semen parameters is usually genetic in origin. Taking medicine like clomid, testosterone or steroid will not improve semen parameters. Male infertility usually necessitates in vitro fertilization treatment, with or without intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
Q: If a couple has been diagnosed as being suffered from infertility, is the chance of
getting pregnant very slim?
A:
No, on the contrary, if you get appropriate management of your infertility problem early, the chance of pregnancy is still pretty high. Although simple advice and measures can help for the initial stage, aggressive treatment may have to be employed at a later stage. According to Nice guideline (Feb2013), in vitro fertilization (IVF) will be offered to women with unexplained infertility, mild endometriosis and mild male infertility who have not conceived after 2 years.
Q: Will I have premature menopause after a few cycles of IVF, since many eggs have been
used up during each treatment cycle?
A:
No. Each woman have 400,000 eggs at puberty and one egg will reach maturity to ovulate every menstrual cycle. There is a total of 400-500 menstrual cycles for the whole reproductive life span. The rest of the eggs will become atretic. Infertility treatment recruits some of the eggs that will regress anyway. Menopause is a stage when all the eggs have naturally regressed and therefore you do not have to worry about premature menopause.
Q: I have tried intrauterine insemination (IUI) for 3 times, why am I still not pregnant?
A:
Usually, IUI is considered a milder form of treatment for infertility if the fallopian tubes are normal. The success rate is around 10 percent per cycle even if gonadotropins injection is employed. You do not have to be discouraged even if you have failed to get pregnant after 3 cycles of IUI. We can employ in vitro fertilization for treatment as the success rate is 3-4times higher than IUI. Some cases do require IVF for success.
Q: Will ovarian stimulation medicine cause ovarian cancer?
A:
Up to date, literature has shown that ovarian stimulation will not increase the chance of ovarian cancer.
Q: What is considered completion of one cycle of in vitro fertilization?
A:
One cycle of ovarian stimulation for in vitro fertilization may result in producing many embryos. For every subsequent cycle, we put back 1-2 embryos into the uterus, if pregnancy has not been achieved. It is not until we have put back all the frozen embryos that it is considered we have completed one full cycle of IVF.
Q: Is the pregnancy rate employing frozen thaw embryos less than fresh embryos?
A:
No. Nowadays, we employ ultra rapid method (vitrification) for freezing embryos, which will not lead to crystal formation that is damaging to the embryos. Moreover, we usually employ natural non stimulated cycle which involves a lower estradiol levels, when we put back frozen thaw embryos and this result in a better pregnancy rate.
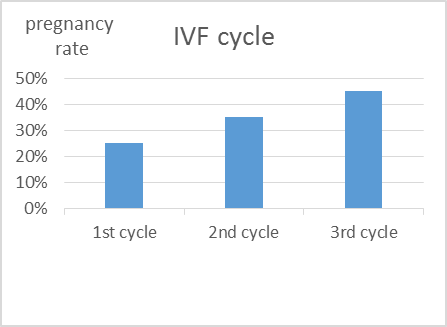
Q: Usually how many IVF cycles should I undergo?IVF
A:
Usually we will advise at least 3 cycles of IVF before giving up as the cumulative pregnancy rate increases. Of course, it depends on assessment after each cycle.
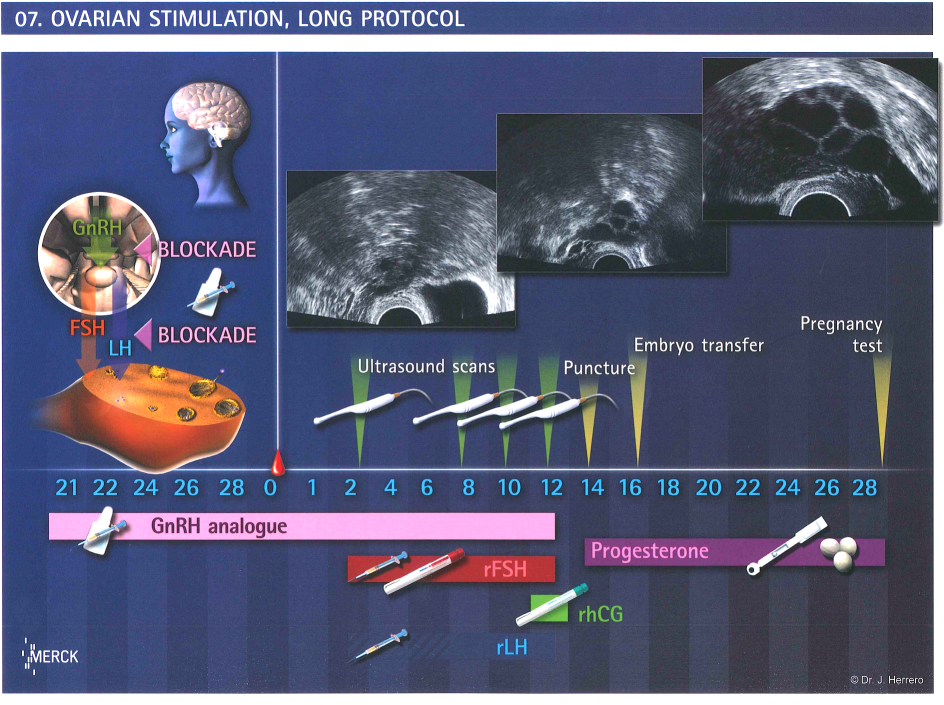
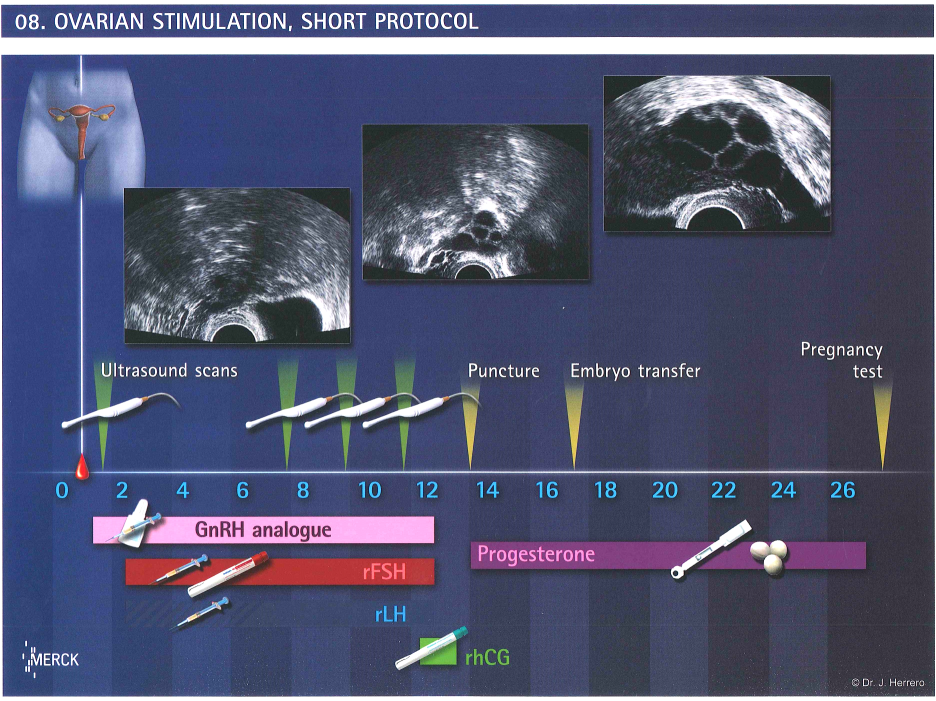
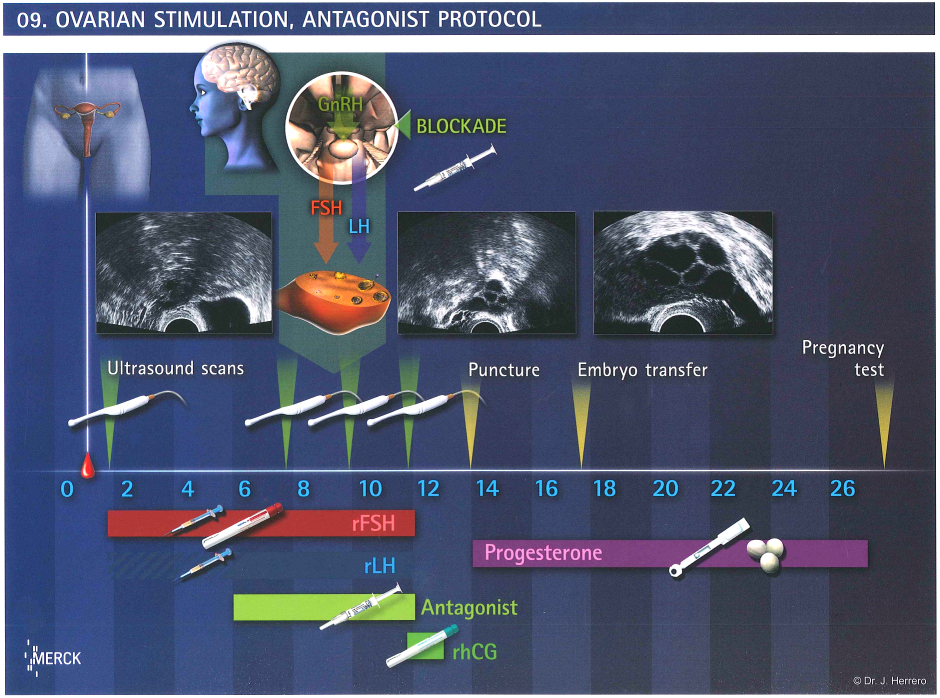
 Ovarian stimulation
Ovarian stimulation