Female Infertility . Ovulatory Problems
How can ovulation be assessed:
26-35 days menstrual cycles are usually considered as normal. The day of ovulation will usually occur 14 days before day 1 of the next menstrual cycle.
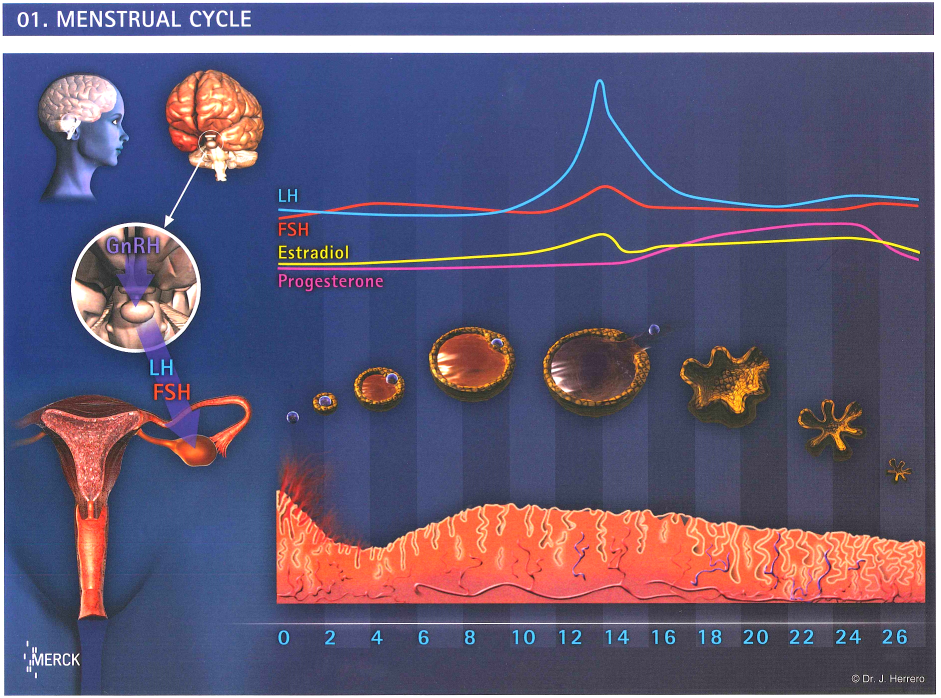
Testing for ovulation:
Blood test and ultrasound studies are accurate in assessing ovulation.
For patients’ convenience, using urine luteinizing hormone (LH) surge stick may help. Sperms take two days to swim up to meet the egg; intercourse after LH surge may miss the optimal day by one day.
- Poor ovarian reserve
Poor ovarian reserve may be caused by age, post-surgery, post-chemotherapy or post-radiation therapy.
Treatment:
ovarian stimulation+ IUI or IVF-ET depending on the situation
- Hypothalamic pituitary cause
Treatment:
gonadotrophin injection
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
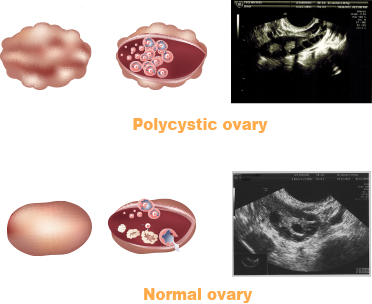 PCOS is a female endocrine disorder of uncertain aetiology, most probably genetic in origin.
PCOS is a female endocrine disorder of uncertain aetiology, most probably genetic in origin.The principle features are anovulation, irregular menstruation and amenorrhea, ovulation-related fertility, excessive amount or effect of androgenic hormones, resulting in acne, hirsutism and insulin resistance. It is also associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes and high cholesterol levels
Diagnostic criteria (Rotterdam, 2003)
- Oligo ovulation and / or anovulation
- Excess androgen activity
- Polycystic ovaries (by ultrasound)
Ultrasound: ≥12 follicles measuring 2-9 mm in diameter in at least 1 ovary.
Treatment:
Clomid
Metformin if there is clomid resistance
Gonadotrophins
Laparoscopic ovarian drilling
- Hyperprolactinaemia
A high blood level of prolactin often causes hypooestrogenism with anovulatory infertility.
Treatment:
dopamine agonist
- Thyroid dysfunction
Both increases and decreases in thyroid function can lead to anovulation and menstrual abnormality.
Treatment: Treatment for hyper/hypothyroidism.
- Sudden dramatic increase or decrease in body weight
- Stress
*For ovulatory problems, if medical treatment fails, go for IVF-ET.